Written By: Dr. Lubna Alshaltoni
Dr. Lubna Alshaltoni is a certified cosmetologist and dermatologist. Having graduated from the American Board Certified in Aestheic Medicine Jordanian Board, and having obtained her post-graduation from the Arab Board Certified Institution in Dermatology and Venerology
Updated On:December 26, 2023
Read more.

Genital herpes is a type of sexually transmitted infection that is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during sexual intercourse or coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person.
What is Herpes?
Herpes is a common infection that affects a large part of the adult population. There are two different types of herpes infection; oral infection and genital infection. It is also important to note that there is no cure for herpes and from the first infectious outbreak, the symptoms will appear. However, each outbreak can be successfully managed with medication.
What are the Symptoms of Herpes Infection?
HSV infection mostly does not present with any symptoms and most people suffering from HSV don’t even realise they have it. Even when herpes infection is symptomatic, the symptoms are very mild. Herpes symptoms appear between 2 to 12 days after exposure to the virus.
The most common symptoms of herpes include, but are not limited to:
- Genital discomfort
- Itching around the genitalia
- Painful blisters or bumps in the genital region
- Blisters that ooze and bleed in the genital region
- Blisters that ulcerate and scab
- Painful urination
- Vaginal discharge
Along with the symptoms affecting the genital region, there might also be general constitutional symptoms such as:
- Swollen lymph nodes, in the groin
- Headaches
- Body pain
- Fever
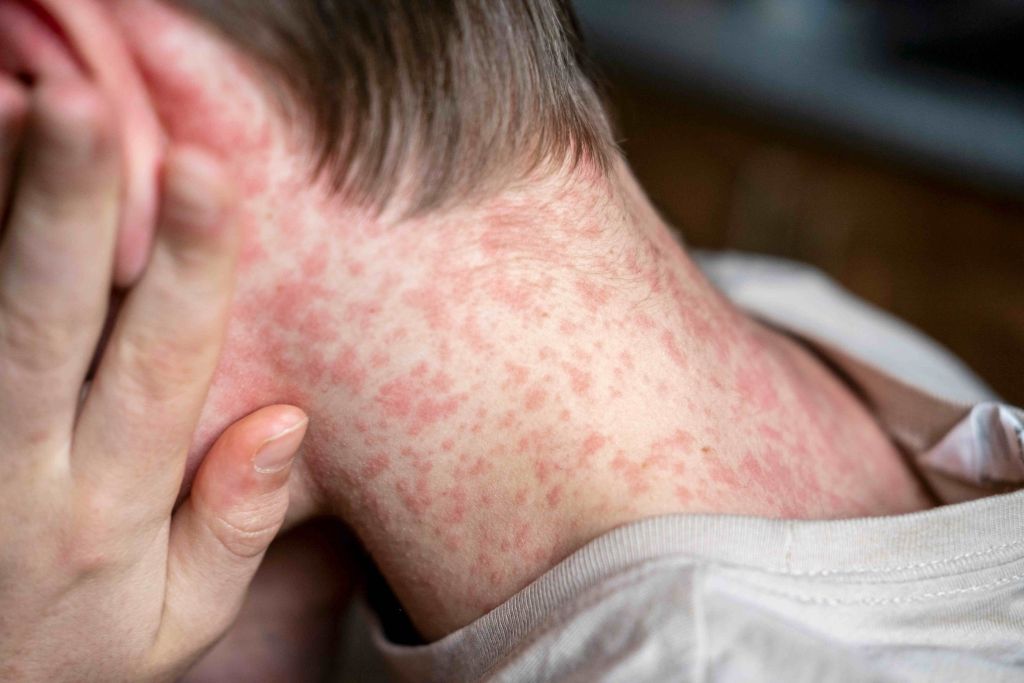
The characteristic rash of herpes infection can occur in other regions of the body and is not limited to the groin.
It can also appear in:
- Buttocks
- Thighs
- Rectum
- Anus
- Mouth
- Urethra
- Vulva
- Vagina
- Cervix
- Penis
- Scrotum
What Causes Herpes?
Herpes is caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and Herpes Simplex Virus 2. HSV 2 is the virus that is responsible for causing genital herpes. HSV 2 is present in blisters and ulcers, or the fluid inside the two, mucosa of the mouth and genital region, and the moist lining of the rectum. It is most often transmitted from one person to another during sexual activity. HSV 1 is more commonly associated with oral herpes which often presents as cold sores and ulcers around the mouth. It is possible for genital herpes to cause oral herpes due to the transfer of the virus from the genital region to the mouth during oral sexual practices.
Children are at risk of HSV 1 infection from coming in contact with an infected individual. This is one of the major reasons it is not recommended for people with a history of cold sores or active cold sores to kiss infants and children. HSV 1 infection in adults is easily manageable and doesn’t require special treatment but the same infection can prove to be fatal for little children.
Risk Factors for Herpes Infection
Herpes is a sexually transmitted infection and as such, the main risk factor for herpes infection is unsafe sexual practices. Participating in unprotected sexual intercourse with multiple partners can increase the risk for herpes and other sexually transmitted infections. Moreover, sexual activity with an infected partner that does not regularly take their medications to manage herpes also puts you at risk of herpes. Given the fact that herpes has no cure and a significantly negative impact on the quality of life, it is highly recommended to reduce the potential risk factors of herpes.
Diagnosis of Herpes Infection
Usually, a physical examination and a history of your sexual activity are enough for your doctor to diagnose genital herpes. Your doctor will probably take a sample from an open sore in order to confirm a diagnosis. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection and HSV-1 or HSV-2 infection are determined by one or more tests performed on the fluid samples. Your blood may be tested too to confirm a diagnosis or rule out other infections. In most cases, a healthcare provider will ask you to get screened for other STIs as well if there is suspicion of herpes. Moreover, they will require your partner to get screened for genital herpes and other STIs too.
Treatment of Herpes Infection
There is no cure for herpes but antiviral therapy can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency of herpes outbreaks. They can also help decrease the intensity of the symptoms to improve the quality of life. Acyclovir and Valacyclovir are the two major antiviral medications prescribed for the management of herpes.
Complications of Herpes
Herpes infection can become complicated and affect different organ systems in the body.Some of the most common complications of herpes include:
Encephalitis.
- HSV can affect the brain and cause it to swell.
- Common symptoms include altered mental status, confusion, and disorientation.
- Neonatal infection.
- A newborn baby can get herpes from the mother when passing through the birth canal.
- The infection can affect the internal organs of the children and can be life-threatening, if severe.
- Eye infection.
- It presents as sores and blurry vision.
- Finger infection.
- This passes from the genital region to the fingers and is medically known as herpetic whitlow.
- Internal inflammatory disease.
- This causes the internal organs to swell and this can cause severe pain and other issues in the body.
Meet our doctors from the Dermatology & Aesthetics department
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
Similar Posts
teleMEDCARE App
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Chronic Care
Know more about our Chronic Care Management Programme in partnership with Damana Saicohealth.

teleMEDCARE App mobile
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Spotii
We have partnered with Spotii to offer a more flexible way to pay - Pay over time for your purchase. No interest, no cost & no catch.