Written By: Dr. Manasi Joneja
Dr. Manasi Joneja is highly proficient in handling, maintaining and deploying emergency medical equipment such as ECHO and TMT, Holter TMT, 2D ECHO, Stress ECHO and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring apparatuses, etc.
Updated On:December 26, 2023
Read more.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a form of the endocrine disease where the thyroid gland overproduces the metabolism-regulating hormone thyroxine (T4). The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland found at the base of the throat & wrapped around the trachea, is responsible for producing thyroxine (T4) & triiodothyronine (T3). Both these hormones play an important role in regulating normal body functions. When the thyroid becomes overactive, it can also negatively impact other processes in the body.
What are the Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)?
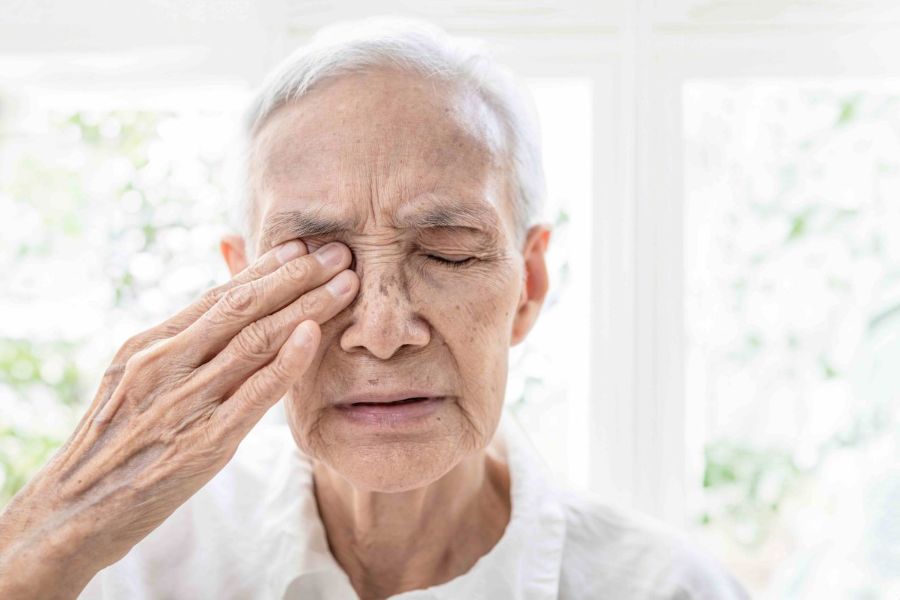
As hyperthyroidism affects multiple body functions, it is sometimes difficult to identify clear symptoms. Patients can manifest one or more of the following symptoms:
- Palpitations & rapid heartbeat
- Weight loss
- Feeling energetic, initially; however as the disease continues, excessive tiredness sets in
- Feeling jittery & nervous
- Increase in appetite
- Frequent bowel movements & diarrhea
- Lack of sleep
- Thinning hair & hair loss
- Cramps in arms & legs
- Hand tremors
- Sensitivity to heat & excessive sweating
- Difficulty in focusing or concentrating
- Irregular menstrual periods
Some more serious symptoms include:
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Heart failure from rapid heartbeats
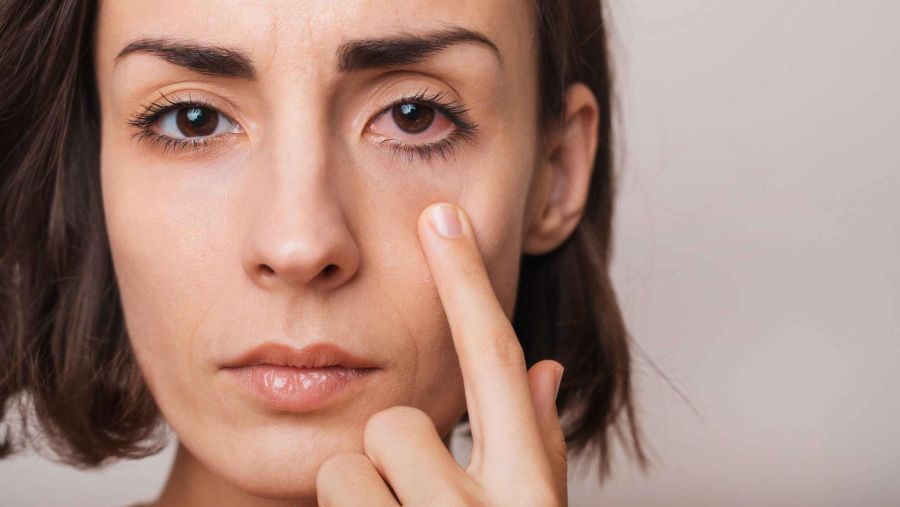
- Exophthalmos (Protruding eyes)
When Should You See a Doctor for Hyperthyroidism?
As some of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism can be easily missed, it is a good idea to see a doctor immediately if you notice excessive weight loss, especially if it is unexpected. Similarly, consult with a doctor if you have palpitations, excessive sweating, or an enlargement/ swelling at the base of your neck.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism?
In a normally functioning thyroid gland, a balanced number of hormones is released to maintain a healthy metabolic rate. In hyperthyroidism, the gland produces too much T4. This can happen due to a number of reasons. These include:
- Thyroiditis or inflammation of the thyroid gland
- Autoimmune related Graves' disease
- Thyroid nodules that produce too much T4
- Postpartum thyroiditis
- Too much iodine in the body because of overconsumption in the diet
- Tumors on reproductive organs like the ovaries or the testes.
- Pituitary gland or thyroid gland benign tumors
- Tumors of the ovaries or testes
- Benign tumors of the thyroid or pituitary gland
- Dietary supplements or consuming too much thyroid hormone medicine for hypothyroidism
How will a Doctor Diagnose Hyperthyroidism?
As hyperthyroidism symptoms can be mistaken for a variety of other issues, the first step in diagnosis involves taking a patient’s detailed medical history. After that, a doctor may also recommend some additional tests. These include:
-
Test to Monitor Cholesterol Levels: A blood test can indicate the levels of cholesterol in your body. Low cholesterol & triglyceride levels are indicative of higher metabolism which is one of the first signs of hyperthyroidism.
-
Thyroid Function Tests: A doctor will also recommend blood tests to get readings for free T4, free T3, & TSH markers. High T4 & low TSH readings are also an indication of hyperthyroidism.
-
Thyroid Scans: Your doctor may order a thyroid scan to see the size, shape & position of your gland. Radioactive iodine is injected into the vein & a special camera is used to take pictures of your gland. Thyroid nodules that take up too much thyroid hormone can be seen clearly in the pictures. When the whole gland takes up radioactive Iodine, it suggests you have Grave’s disease. You should take up this test if you are pregnant or breastfeeding even though the amount of radiation needed for the scan is small.
-
Ultrasound: Ultrasound of thyroid gland helps to look at the gland more closely, it helps to look at the nodules/lumps in the gland & gives some due if the nodules could be cancerous.
-
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test: It helps to check thyroid function & find the cause of hyperthyroidism. For this test, you will be asked to swallow a small amount of radioactive iodine in liquid or capsule form. A device called gamma probe will be placed in front of your neck. The probe measures how much radioactive iodine your thyroid takes up from the blood. Even though the test uses a small amount of radiation, you should not do this test if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
What are the Risks Associated with Hyperthyroidism?
As immune system-related disorders run in families, a genetic predisposition towards hyperthyroidism can manifest as Graves’ disease. Some of the other autoimmune diseases associated with hyperthyroidism include:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Pernicious Anemia
- Primary adrenal insufficiency
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Celiac disease
- Vitiligo
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
What are the Complications Associated with Hyperthyroidism?
Some complications arising from hyperthyroidism include:
-
Heart Disease: It can cause rapid & irregular heartbeat that can lead to blood clots or heart failure.
-
Osteoporosis: High amounts of thyroid hormone in the blood can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium & other minerals into the bones. Over time, untreated hyperthyroidism can cause osteoporosis, weak bones, & fractures.
-
Eye-related Problems: Eye problems, thyroid eye disease, or Graves’ ophthalmopathy is the name given to patients who develop bulging, red, & swollen eyes as a result of hyperthyroidism. These patients also have an increased sensitivity to light, blurring, & double vision. If left untreated, over time, severe eye problems can rarely lead to a loss of vision.
-
Skin Problems: Another complication of hyperthyroidism is Graves dermopathy—a condition where the skin on the shins & the feet turns red with swelling. It causes severe dryness & itchiness.
-
Thyrotoxic Crisis: In rare cases, symptoms of hyperthyroidism can get more serious, leading to a high fever, palpitations, & delirium.
What are the Treatments Available for Hyperthyroidism?
There are many ways to treat hyperthyroidism depending on a variety of factors. These include:
- Your age
- The severity of the symptoms
- The reason for the hyperthyroidism
- Other related conditions like pregnancy or heart disease
Depending on your preferences a doctor can prescribe multiple treatment options. These include:
Anti-Thyroid Medication Therapies
Milder cases of thyroid disorders can easily be treated with medicines that stop making excess hormones. Doctors usually prescribe carbimazol Tapazole & propylithiouracil, where symptoms begin to improve a few weeks after starting treatment. Patients taking these medicines need to be mindful of side effects, some of which include skin rashes, hives, fevers, & joint pain.
Treatment Through Radioactive Iodine
Patients with hyperthyroidism can take radioactive iodine to destroy the cells that produce excessive thyroid hormones. The iodine is taken via the mouth & absorbed by the thyroid glands that are causing overactivity. Sometimes, the therapy can also result in an underactive thyroid & patients who have undergone radioactive iodine therapy will need to take a small amount of thyroxine to replace the reduced levels of thyroid hormone.
Treatment with Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers do not stop thyroid hormone production, but they can help treat some of the symptoms, such as the tremors & palpitations that are associated with the disease.
Thyroidectomy
Patients who do not qualify for radioactive iodine treatment or medication may consider surgical removal of the thyroid gland as a more permanent course of treatment. A part or most of the thyroid gland can be removed. A patient will have to take oral thyroid hormone replacement for the rest of their life.
What are Some Home Remedy Solutions for Hyperthyroidism?
Some home remedies & lifestyle adjustments that can help combat the symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
-
Diet Changes: Cutting out excess iodine from the diet, especially in the form of iodine-supplemented salt, & food rich in iodine like kelp, dulse, & other types of seaweed can be helpful.
-
Exercise Regularly: Exercise can help you improve muscle strength & toning while regularly working out with weights helps maintain bone density.
-
Treating Graves' Ophthalmopathy or Dermopathy: You can treat dry itchy eyes & skin with lubricating eyedrops & gels. Sunglasses help combat light sensitivity. However if symptoms are more, your doctor may prescribe some medicine including steroids. In severe cases, surgical options for eye may be considered.
Can Hyperthyroidism be Prevented?
As hyperthyroidism, especially Graves’ disease, has a genetic correlation, it cannot be prevented. In certain cases, especially during or after pregnancy when there is a surge in thyroid activity & hormone production, a latent predilection for the disorder can manifest itself & timely medical intervention is needed.
If a family member has Graves’ disease or hyperthyroidism, it is a good idea to talk to a doctor & get yourself frequently tested. Similarly, patients with type 1 diabetes, pernicious anemia, & immune system disorders should have themselves regularly tested & monitored for hyperthyroidism.
If you feel that you may be suffering from hyperthyroidism, it is advisable to get in touch with a medical professional. Our experts are always an appointment away to guide you with the right thyroid treatment plan
Meet our doctors from the Internal Medicine department
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
Similar Posts
teleMEDCARE App
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Chronic Care
Know more about our Chronic Care Management Programme in partnership with Damana Saicohealth.

teleMEDCARE App mobile
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Spotii
We have partnered with Spotii to offer a more flexible way to pay - Pay over time for your purchase. No interest, no cost & no catch.