Written By: Dr. Usama Saleh
Dr. Usama Hassan Saleh, an orthopedic & trauma surgeon, graduated from Medical school in Egypt, did his clinical fellowship training in upper extremity surgery at the University of Toronto, Canada & is holding membership of The Royal College of Surgeons of England (MRCS UK) Diploma.
Updated On:December 22, 2023
Read more.
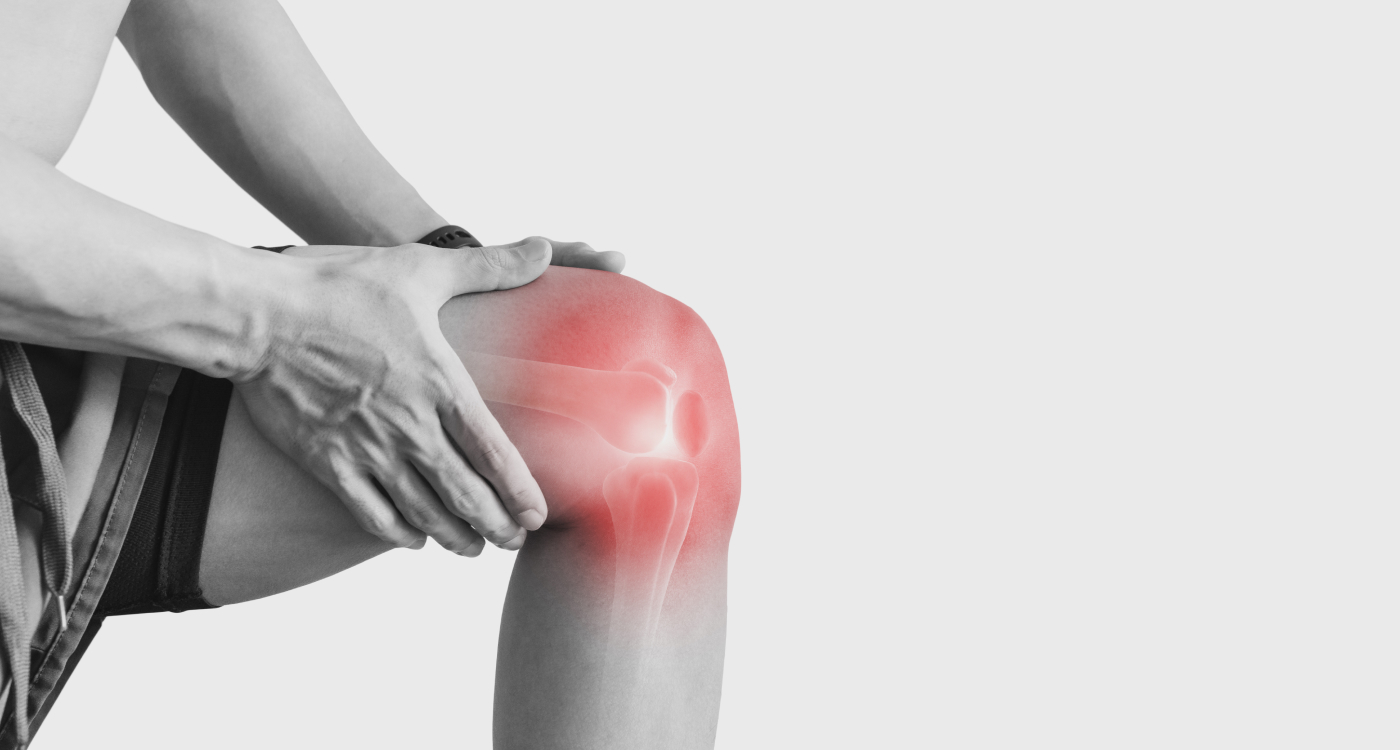
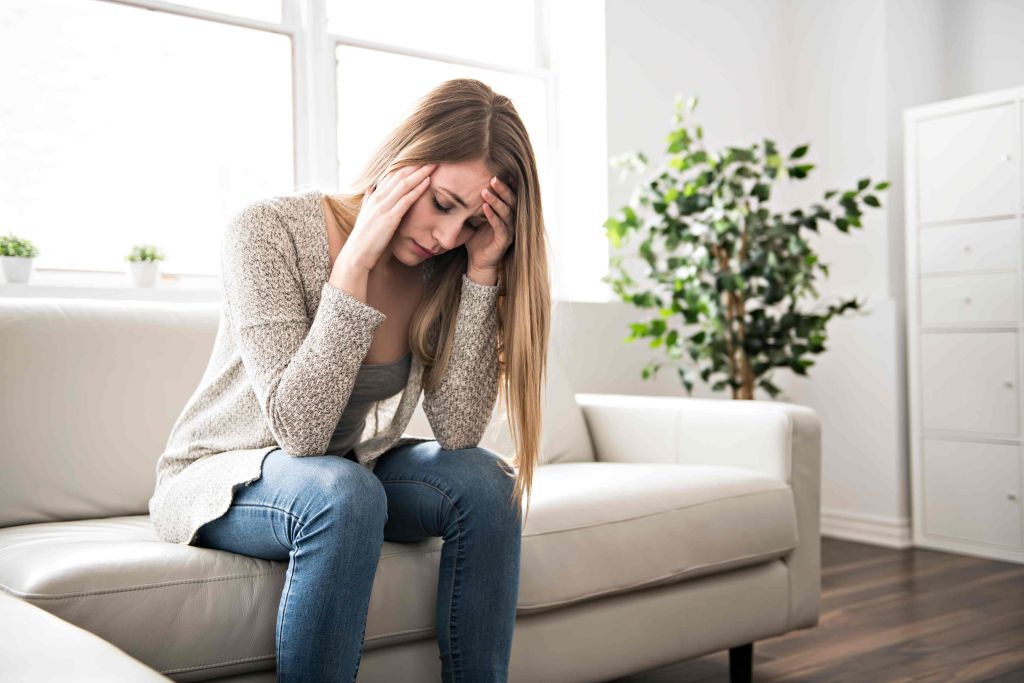
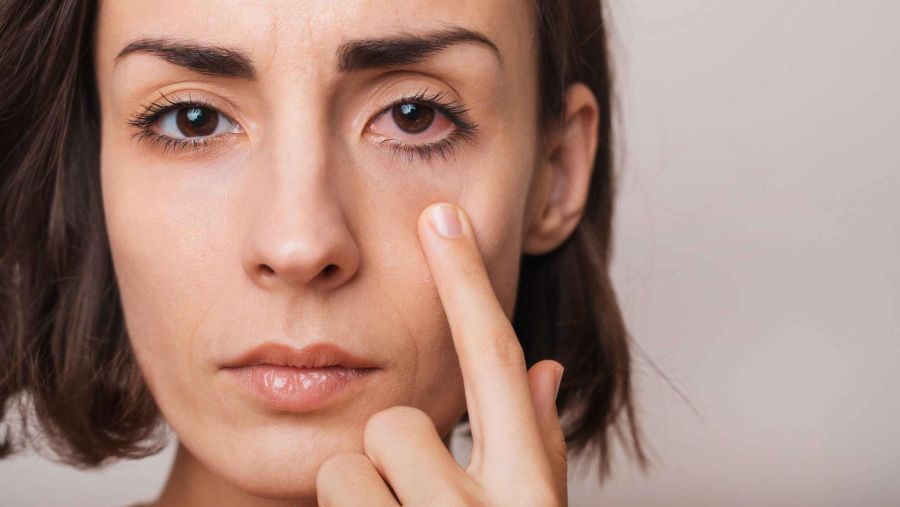
An Overview of Knee Pain
Knee pain affects about 25 percent of adults1, although people can experience knee pain at any age. Knee pain can be a result of injury such as ligament injury or torn cartilage, or a symptom of conditions such as arthritis, gout, and infection. Among people aged 50 years and older, the most common cause of knee pain is osteoarthritis. The cause of knee pain determines what treatment plan is administered.
Types of Knee Pain
Broadly, knee pain is divided into two categories based on the underlying causes:
- Acute injury: This includes a fractured bone, torn ligament, acute tendonitis, damaged cartilage or the most serious condition of acute infection.
- Chronic causes of knee pain : This includes osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis patellar pain syndromes, chondromalacia, and IT band syndrome.
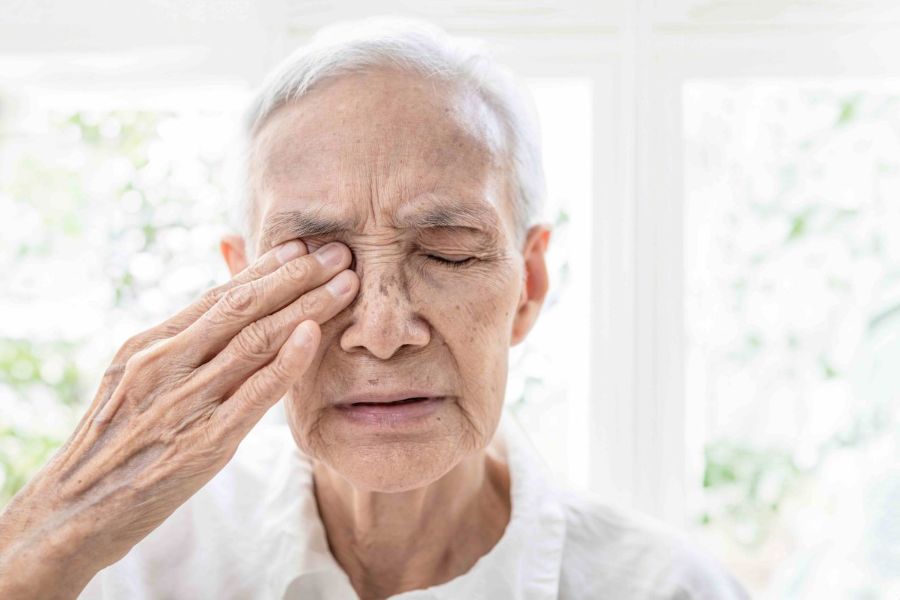
Symptoms of Knee Pain
Exact symptoms may vary depending on the cause of the knee pain, but generally patients experience:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Limited mobility
- Stiffness
- Popping sounds
- Others
When To Call Your Doctor
Contact your doctor if you experience the following:
- Knee pain and discomfort
- Inability to bear weight on your knee
- Instability on the knee, i.e. it gives out when you stand or walk
- Considerable swelling
- Inability to fully extend the knee
- Noticeable deformity in the knee
Risk Factors for Knee Pain
- Biomechanics: Changes in walking style, or incorrect form whilst lifting heavy weights, can make one more likely to get knee pain.
- Being overweight: The greater the stress placed on the knee joint, the greater the likelihood for pain.
- Repetitive movements: Kneeling for too long or doing certain activities like cycling, skiing, and running can predispose one to knee pain.
- Previous injury: Previous injuries such as ruptured ligaments or damaged cartilage can cause knee pain in the future.
- Incorrect exercise form: Performing squats with an incorrect form can shift the load from the muscles onto the knees, leading to an increased risk of injury and knee pain.
- Low flexibility: A lack of regular movement and flexibility can also shift the load off the muscles and onto the knee joint while performing tasks such as walking, running, lifting something, and bending down.
Causes of Knee Pain
Knee pain caused by acute injury to the knees
- Fractures: When a bone is directly struck with significant force, it can cause one or more of the bones in the knee to break, causing a fracture. Fractures are a very common knee injury and are quite painful. They interfere with proper knee function and make it harder to lift weight. Fractures require immediate medical attention.
- Ligament injuries: The most frequently occurring ligament injury is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. It typically affects athletes as it is caused by sudden stopping and rapid changes in direction, for example when playing football. The posterior cruciate ligament and lateral collateral ligament can also get injured, although not as frequently.
- Meniscus injuries: The medial and lateral menisci are the knee’s shock absorbers composed of cartilage that can get damaged when the knee is twisted.
- Dislocation: This injury is very serious and requires immediate medical care. The dislocated joint can restrict blood flow to the leg and cause further harm.
Knee pain caused by medical conditions
Autoimmune conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune conditions can affect joints in the body including the knee joint, causing pain, discomfort, and swelling.
Gout: Another type of arthritis that commonly affects a person’s big toe, gout can also cause flare ups in the knee. These can be very painful and render sensations of burning in the affected area.
Infections: These can sometimes lead to a condition called septic arthritis. In this condition, the knee can become infected, causing pain and swelling. The patient will also develop a fever. Septic arthritis requires antibiotics for treatment.
Knee pain caused by chronic overuse syndrome
- Osteoarthritis: This is another chronic overuse condition where the cartilage of joints is worn down due to use over time and age.
- Patellar tendinitis: People who repeatedly perform the same movement over time can develop this. The condition is common among runners and cyclists. The chronic repeated movement of the joint causes degeneration and hence leads to the tendons that connect the kneecap to the shinbone to become inflamed.
- Bursitis: Under the skin and above our joints exist sacs that contain fluid. These bursa sacs reduce friction between the mobile parts of our joints. When these sacs above the kneecap become inflamed due to repeated movement of the joint, it causes swelling and inflammation i.e. bursitis.
- IT (iliotibial) band syndrome: The IT band is a tissue that connects the hip to the knee, and it can become inflamed due to overexertion. This condition causes pain on the outer part of the knee.
- H3 – Knee pain caused by Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition that children can develop. As their bones and joints are still in the developing stage, a bump can form below the knee. Overexertion and irritation, through exercise for example, can cause pain to the area called tibial tubercle.
Knee Pain Treatment
As mentioned earlier, the treatment for knee pain varies based on its underlying cause:
- Medication: Mild knee pain can be treated with over the counter anti-inflammatory pain medication. However, do see a doctor to get diagnosed for the underlying cause. Doctors may also prescribe medications to treat that cause.
- Injections: Sometimes medication is directly injected into the knee. Corticosteroids and lubricants are the most commonly injected substances. Corticosteroids are injected every few month and can help treat the arthritical inflammation of the knee. Lubricants help in joint mobility as their composition is similar to that of joint fluid.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help with movement and stability as the muscles in the leg are strengthened to support the body’s weight such that it does not fall directly onto the knees.
- Surgery : Arthroscopic knee surgery is a fairly common procedure through which the physician can diagnose the cause of the knee pain as well as repair minor injuries.
- Partial knee replacement is another surgical option. In this procedure the surgeon replace the damaged compartment of the knee and replaces it with synthetic parts composed of both plastic or metal.
- Total knee replacement surgery is performed in the most severe cases where all the compartments of the knee are damaged . An artificial joint replaces the entire knee.
Home Remedies for Knee Pain
Over the counter pain relief drugs can be useful for the short term. In cases of an injury or a gout attack, it is helpful to remember RICE:
- Rest
- Ice
- Compress
- Elevate
Take a rest from whatever you are doing and avoid exerting the knee joint. Ice the area frequently to relieve inflammation. Use a compression bandage to limit swelling and aid with knee alignment. Also, elevate the leg as you rest it.
Exercises to relieve knee pain
Certain exercises can help strengthen your leg muscles and improve flexibility so that while you move, your body weight does not fall onto the knees.
Stretching exercises
- Heel and calf stretch
- Quadriceps stretch
- Hamstring stretch
Strengthening exercises
- Box squats
- Calf raises
- Hamstring curl
- Leg extension
- Glute bridges
Knee Pain Prevention
There are multiple ways to prevent knee pain, as well a knee injuries, including:
- Maintaining your ideal weight to avoid increased stress on your knees.
- Wearing the right shoes to ensure correct leg alignment and balance.
- Warming up before beginning physical activity, including stretching the front and back of your thighs, to decrease tension on your tendons and relieve pressure on your knees.
- Doing exercises that have low impact on your knees, like swimming or walking, as opposed to running.
- Using the elliptical or rowing machine instead of the treadmill to again, ensure low impact on your knees.
- Weight training to strengthen your leg muscles to better support your knees and avoid injuries.
Complications of knee pain
Serious injuries like dislocation of the knee joint, if not handled swiftly, can cause serious problems by restricting blood flow to the leg. Gout, if left untreated, can cause permanent damage to the joint. Most of the complications arise in the long run when medical care is not sought out and the underlying cause of the pain is not diagnosed and treated. To find out more about the symptoms, causes, and treatments of knee pain, get in touch with us.
Meet our doctors from the Orthopaedics department
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
Similar Posts
teleMEDCARE App
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Chronic Care
Know more about our Chronic Care Management Programme in partnership with Damana Saicohealth.

teleMEDCARE App mobile
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Spotii
We have partnered with Spotii to offer a more flexible way to pay - Pay over time for your purchase. No interest, no cost & no catch.