Written By: Dr. Mohamed Ghanem
Dr. Mohamed Ghanem is a Specialist in the Department of Orthopaedics at the Medcare Orthopaedics & Spine Hospital and the Town Square branch of Medcare Medical Centre.
Updated On:December 28, 2023
Read more.

What are Shin Splints?
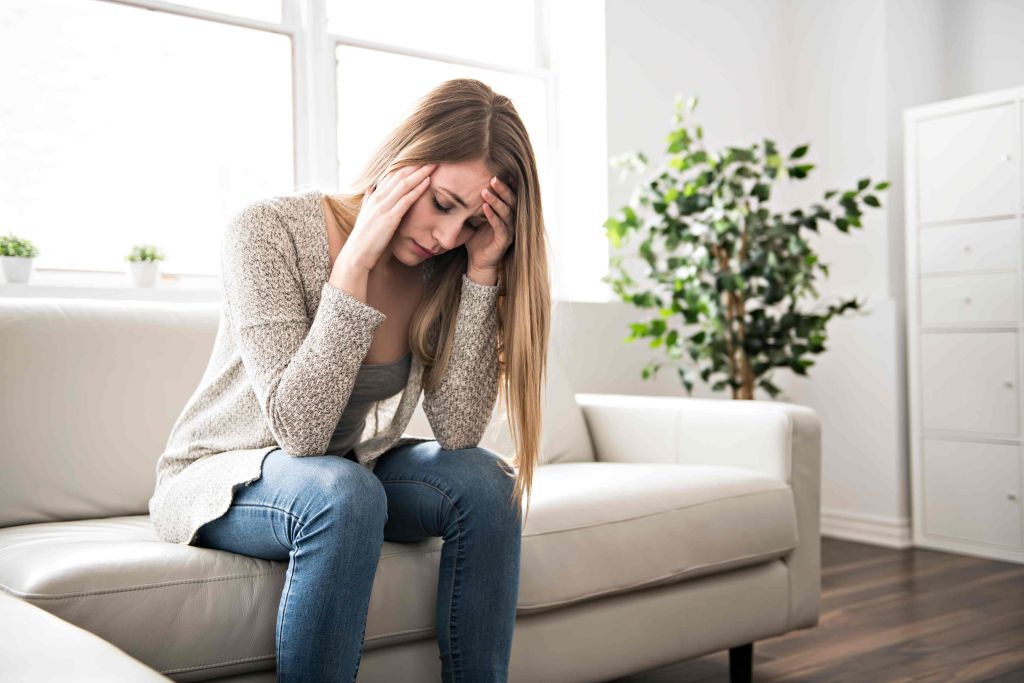
Shin splints are a term used to describe pain in the front of your lower legs. The muscles, tendons, and tissue surrounding your shin bone (tibia) become inflamed, resulting in this pain. Because their shin bones, muscles, and connective tissues are repeatedly stressed, athletes frequently experience shin pain. Shin splints are sometimes referred to as medial tibial stress syndrome by medical professionals.
An extremely frequent overuse injury is shin splints. Most sufferers with shin splints recover without any long-term health issues with rest and ice. Shin splints do, however, have the potential to turn into a tibial stress fracture if neglected.
Causes of Shin Splints
Shin splints are caused by the pulling and tearing of the muscles and connective tissues in your lower leg, which repeatedly stresses your shin bone. Your shin bone may weaken and become inflamed as a result of repeated, frequent pressure from running and jumping. If the damage to the bone is not given time to heal, it may worsen and become extremely painful. Many things, such as beginning a new workout regimen or rapidly increasing your level of physical activity, might cause such recurring stress.
Symptoms of Shin Splints
Lower leg soreness and pain are the most typical symptom of shin splints. Your shin bone could feel painful to the touch and the pain might range from minor to severe. Also possible is a slight swell.
Symptoms of Shin splint include:
- A sharp or throbbing pain
- Intermittent discomfort during exertion, developing into a continuous, enduring pain even after the action has stopped.
- Commonly felt on the front of the shin bone or the inner lower portion of your leg
- Worsening pain after exercise
When to see a doctor for Shin Splints?
If your shin discomfort is severe or doesn't go away after a few weeks of rest, you should contact your doctor. If your legs are really painful, red, or swollen, call your healthcare practitioner. These signs could point to an infection or another ailment.
Shin Splints Risk Factors
Shin splints can affect everybody, although some people are more susceptible than others. Shin splints are more common in certain demographics, such as:
- Anyone who suffers from an underlying vitamin D deficiency, an eating disorder, or a lack of regular menstrual cycles
- Athletes who engage in high-impact activities that put a strain on their legs
- Dancers
- Military personnel and those who frequently march or walk
- People who cover long distances on foot
- People who exercise in non-supportive footwear
- People who may already have weakened bones due to osteoporosis
- People with high arches, flat feet, or stiff arches. Your muscles and bones may not be able to distribute or absorb force from impact and loading activities in these circumstances.
- Runners, especially those who abruptly up their running regimen or run on unlevel surfaces
Shin Splints Complications
Shin splint complications are uncommon. Shin splints can become stress fractures if you keep exercising or playing sports without giving your legs time to recover. Little fissures develop in your bone and become stress fractures. When treating a stress fracture, medical professionals frequently advise using crutches or donning a walking boot until the bones repair.
Shin Splints Diagnosis
A physical exam and knowledge about your medical history help doctors identify shin splints. Your doctor will assess your gait as well as your lower leg, ankle, and foot. A thorough examination will involve moving your ankle and foot and feeling along the bone for any soreness. To identify shin splints or a stress fracture, try standing on the sore leg or hopping on it.
Your doctor will initially request an X-ray to rule out a stress fracture, even though stress fractures aren't visible in around two-thirds of conventional X-rays. In light of this, if your healthcare professional has cause for worry, they can then request an MRI or bone scan. Due to the fact that they detect the damage before an X-ray, these tests enable your doctor to determine whether the shin splint has developed into a stress fracture.
Shin Splints Treatment
You must give your muscles and bones time to recover if you want to get rid of your symptoms. Treatment for shin splints typically consists of a mix of:
- Give your muscles and bones time to heal by taking a break from sports, running, and other activities. For a few weeks or longer, you might have to take it easy and rest.
- For a few days, apply a cold compress to your shins three to four times per day, every 10 to 20 minutes. Shin splints' pain and swelling can be reduced with ice.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) sold over the counter (OTC) can reduce pain and swelling.
- A daily dose of 1000–2000 IU of vitamin D3 may be beneficial. Discuss dietary supplements with your doctor.
- Stretching and flexing your lower leg muscles gently may assist with shin splints.
- To lower the chance of getting shin splints again, gradually increase your activity level.
- Inserts (orthotics) can effectively relieve the pain of shin splints in those with flat feet. By supporting your arches, orthotics eases the strain on the bones and muscles in your lower legs.
- By strengthening your legs and lowering your risk of suffering another injury, physical therapy can help you regain your mobility.
Shin Splints Prevention
Shin splints may not always be preventable, but you can lessen your chance of getting them or having them get worse. Your risk can be decreased by:
- Shoe support is important when working out. Every 300 miles, your running shoes should be replaced. Consider putting on arch-supporting orthotic inserts. You might also think about consulting a pedorthist. A pedorthist is a professional who specializes in using shoes and other types of footwear to treat issues with your lower legs and feet.
- Increase your activity level and intensity gradually as you get started. Avoid spiking your activity levels.
- Warm up your muscles by stretching them before working out.
- When running, stay away from hard, uneven, or mountainous surfaces. If you run frequently, think about including low-impact exercises (like swimming) in your fitness regimen to relieve the strain on your legs. Take into account cross-training and vacation days.
- Between activities, take a break to give your muscles and bones a chance to recover.
- Listen to your pain. Reduce your exercise level till your shin pain subsides if you are experiencing it. Avoid attempting to endure discomfort.
References
Bates, P. (1985). Shin splints--a literature review. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 19(3), 132-137.
Carr, K., & Sevetson, E. (2008). How can you help athletes prevent and treat shin splints?.
Rasmussen, W. (1974). Shin splints: definition and treatment. The Journal of Sports Medicine, 2(2), 111-117.
Thacker, S. B., Gilchrist, J., Stroup, D. F., & Kimsey, C. D. (2002). The prevention of shin splints in sports: a systematic review of literature. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 34(1), 32-40.
Tolbert, T. A., & Binkley, H. M. (2009). Treatment and prevention of shin splints. Strength & Conditioning Journal, 31(5), 69-72.
Meet our doctors from the Orthopaedics department
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
Similar Posts
teleMEDCARE App
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Chronic Care
Know more about our Chronic Care Management Programme in partnership with Damana Saicohealth.

teleMEDCARE App mobile
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Spotii
We have partnered with Spotii to offer a more flexible way to pay - Pay over time for your purchase. No interest, no cost & no catch.