Written By: Dr. Ravinder Verma
Dr. Ravinder Verma is an ENT specialist with an MBBS from AFMC (Armed Forces Medical College) – Pune where he has also worked as an examiner. He has earned his DNB & MS, from the MUHS (Maharashtra University of Health Sciences).
Updated On:December 21, 2023
Read more.
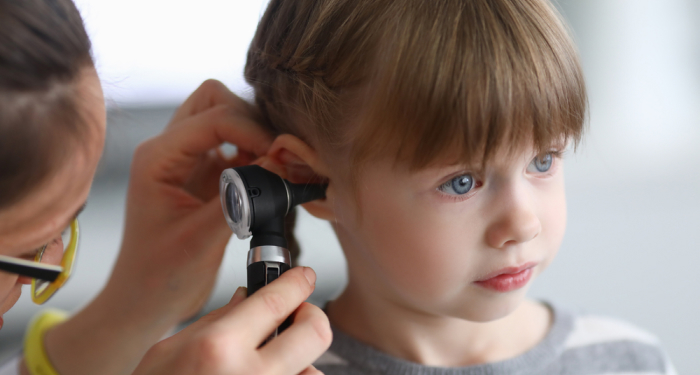
What is an Ear Infection?
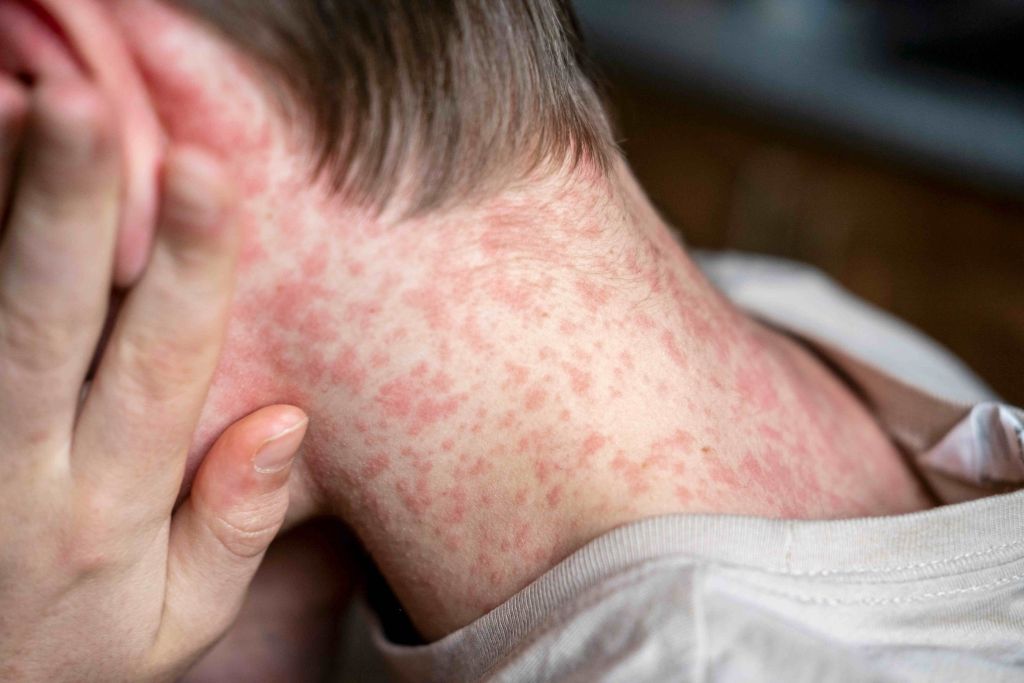
It is the infection of the outer, middle, inner ear or the bone around the ear by bacteria, virus or fungus. Ear infections are quite common in children but can affect all ages as well.
Common symptoms of an Ear Infection
- Earache
- Impaired Hearing/loss of hearing
- Ear discharge/bleeding from ear
- Dizziness/Impaired balance
- Feeling of blockage/Pressure inside the ear
- Redness/swelling of skin of outer ear
- Tenderness/Pain on touch or pressure on the outer ear
- A high temperature
- Pain in ear on swallowing/going up & down a fast elevator/during a flight take off/landing abnormal sounds in ear
When to see a doctor for an Ear Infection?
If you are having severe pain in the ear that is not settling with off-the-counter pain killers for two days &/or is associated with other symptoms like redness/ tenderness to touch/ swelling of the ear or around it (especially in children) that interfere with your ability to perform day-to-day functions, we advise that you get a consultation with an Ear, Nose, & Throat (ENT) specialist. On its own, ear discharge or impairment in hearing, or dizziness merits a visit to an ENT Specialist as soon as possible in order to rule out long term complications.
Causes of Ear Infections
An ear infection is caused by bacteria, virus or fungus or multiple/mixed infections. Some factors that trigger ear infections are dampness in the ear, habits like ear picking/scratching, use of ear buds to clean ears, regular use of headphones or ear plugs for long durations, use of dirty linen/towels, etc.
The medical cause of Ear Infections are:
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Fungus
In everyday life Ear Infections can be caused by:
- Excessive ear cleaning - the most common cause is scratching, trauma during cleaning.
- Changes in air pressure or weather - Sudden pressure changes can injure the ear drum especially during rapid descent of flight/ rapid ascent during professional/ recreational diving which can cause bleeding &/or rupture of ear drum that can get infected.
- In children faulty position during feeding as well as upper respiratory infection can cause infection in middle ear which is dangerous & distressing to the child.
- Upper respiratory tract infections- often occurring during a cold or flu.
- Swimming in contaminated water.
- Gyms; Parlors; Use of ear buds/ ear plugs/mufflers.
Types of Ear Infections
There are six main types of ear infections depending on the part of ear involved & spread to other parts. They can present as single or a combination of various symptoms.
-
Glue Ear (Serous Otitis Media): Ear infection caused by the buildup of pus/ fluid in the middle ear. It is most common in babies & toddlers & may go undetected with incomplete treatment or inability to follow up with an ENT specialist who has the medical kit to look for this particular sequelae.
- Outer Ear Infection (Otitis Externa): Caused by bacteria or fungus. It affects the external visible part of ear that is pinna, ear canal & the ear drum. It is also called Swimmer’s Ear & can be caused by the buildup of bacteria; brought on by water being left behind in the ear canal after a swim/ bath.
- Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media): Bacterial/viral infection is most common in childhood & is caused by recurrent colds, sore throat/ tonsillitis & a blockage of the tubes between the middle ear & upper throat through which the infected secretions travel up into the middle ear & can cause long term complications if not managed vigorously. The ear drum may rupture & may not heal leading to recurrent ear discharge & diminished hearing. This may need surgery to repair at a later date if not prevented with early medical treatment.
- Vestibular neuronitis: A viral infection can affect the vestibular nerve that is responsible for balance of the body leading to loss of balance/dizziness, nausea, vomiting.
- Myringitis: Infection of the ear drum caused by bacteria or a virus, causes inflammation/ swelling & formation of painful blisters.
- Acute mastoiditis: This serious ear infection affects the bone just behind the ear & is very common in childhood. Urgent use of antibiotics & follow up with ENT Specialist is recommended.
Some ear infections, if left untreated, can lead to avoidable complications- like chronic pain; recurrent ear discharge due to residual or persistent infection; rupture of ear drum; diminished hearing; adhesions of the small bones of the ear; persistent fluid/ glue in ears in children leading to impairment of hearing & balance. If your symptoms persist longer than 2 to 3 days, please visit a Medcare doctor/ ENT Specialist Surgeon.
Stages of an Ear Infection
Mild, moderate or severe infection depends on various factors including age, general health & immunity of individual. There are no clearly defined stages of an ear infection, but a worsening of symptoms can indicate that the condition is advancing & may lead to complications/ sequelae. If your symptoms persist & are interfering with your quality of life, seek medical care early.
Ear Infection Risks & Complications
If left untreated, ear infections can lead to medical complications like:
- Mastoiditis: This is a rare inflammation of a bone close to the ear. It is a serious bacterial infection that is more common in children than adults. Invasive measures need to be taken to treat mastoiditis; including surgical draining of the middle ear & mastoid air cells from the bone.
- Perforated Eardrum: A serious ear infection can lead to a damaged or ruptured eardrum, causing hearing loss, ear discharge, & earache. Perforated eardrums may heal on their own if infection is kept in check by early intervention but in some cases will need surgery to repair the eardrum / small bones of the ear to improve/restore hearing.
- Loss of Hearing: Ear infections cause a buildup of fluid in the ear, resulting in temporary but, in some cases, potentially long term hearing loss.
- Chronic Vertigo: Vertigo or impaired balance can be caused by a viral infection. Usually it is temporary but may be recurrent if the treatment is delayed.
Can chronic Ear Infections cause hearing loss?
Long term or repeated ear infections may lead to the buildup of fluids in your ears & significantly affect your hearing. Hearing loss occurs in the case of permanent damage to the ear drum &/or the small bones in the middle ear.
Ear Infection Treatment
Mild ear infections may be self-limiting with supportive pain killers & removal of cause of infection. Common infection treatments may include :
- Antibiotics
- Antihistamines/Decongestants
- Antibacterial/antifungal Ear drops
- Painkillers/Anti-inflammatory medication
- Ear packs &/or drainage of pus/fluid
Some more ear infection treatments include:
- Glue Ear (Serous Otitis Media) Treatment: Usually affects children, & serous fluid in the middle ear is managed with antihistamines/ decongestants. If it doesn’t resolve within one to three months, a procedure is done to remove fluid from the middle ear with or without placement of ventilation tubes along with removal of adenoids if they are enlarged. So a follow up with ENT Specialist is desirable.
- Outer Ear Infection (Otitis Externa) Treatment: Antibiotic ear drops with supportive management for pain / itching along with oral antibiotic if necessary is the best approach.
- Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media) Treatment: Middle ear infections almost always will need antibiotics along with anti-inflammatory medication for seven days. Again one has to keep track of recurrence & sequelae if any.
- Vestibular Neuronitis Treatment: Symptoms of vestibular neuronitis are managed with prescribed medication to calm vertigo & nausea. If vomiting persists, intravenous fluids may be administered. To help patients recover & reacquaint themselves with balance, physical therapy may be prescribed.
- Infectious Myringitis Treatment: Antibiotics are prescribed to treat infectious myringitis. In some cases, small cuts may be made on the blisters to drain its fluid alongside medication for pain.
- Acute Mastoiditis Treatment: This is a serious condition, & ENT Specialist must be consulted as soon as possible to start the course of treatment. Acute mastoiditis is treated with injectable antibiotics & may also require a procedure to drain the middle ear/mastoid (Bone behind the ear).
Treatment for Chronic Ear Infections in Adults
Chronic ear infections in adults can be treated with antibiotics, drops, pain relievers, antihistamines. Complications & sequelae are treated with surgery to repair the eardrum / small bones of the ear to improve/ restore hearing & drilling of mastoid bone to remove the infection by establishing drainage into the middle ear.
Home Remedies for Ear Infection
Most cases of ear infection recover on their own if one maintains hygiene, no touch policy together with home remedies to help relieve pain & discomfort. If symptoms persist, the infection could advance & lead to medical complications. It is recommended to consult an ENT Specialist surgeon if symptoms do not improve over a period of time.
- Olive Oil: A few drops of warm olive oil will soothe earache if due to accumulated wax. Wax solvents from over-the-counter (OTC) pharmacies will be a preferred choice.
- Cold & Warm Compresses: Alternating between cold & warm compresses will calm ear & headaches in children & adults but it is nonspecific & does not address the issue of infection comprehensively.
- Sleeping Position: It is important to avoid any added pressure to the ear while it is infected or healing. Try to sleep with the infected ear raised.
- Pain Relievers From a Pharmacy: Earache & headaches can be managed with common over-the-counter (OTC) painkillers & decongestants.
Ear Infection Prevention
Ear infections are tedious & painful. You can prevent them by:
- Thoroughly drying your ears after a bath or shower: Use a clean towel or tissue to carefully dry your ears, preventing a moist atmosphere for bacteria.
- Using earplugs when you swim: Fluid retention in the ear can lead to Swimmer’s Ear in some. If you are a regular swimmer, & have had issues then consider using earplugs & if you do, keep them clean each time. Normal individuals do not need to wear plugs for swimming as they have natural drainage to outside.
- DO NOT Use cotton buds: Using a cotton bud with great force or lack of attention can cause minor injuries & lead to an ear infection.
- Be mindful about what your ears come in contact with: Use clean towels & pillowcases, sanitised earphones, & avoid swimming in dirty water.
Your health is at the heart of what we do. Our ENT experts are always an appointment away to guide you through the right treatment plan.
Meet our doctors from the Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) department
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
Similar Posts
teleMEDCARE App
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Chronic Care
Know more about our Chronic Care Management Programme in partnership with Damana Saicohealth.

teleMEDCARE App mobile
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Spotii
We have partnered with Spotii to offer a more flexible way to pay - Pay over time for your purchase. No interest, no cost & no catch.