Written By: Dr. Ramamurthy
Dr. Ramamurthy Lakshminarayanan is an ENT specialist at Medcare. He completed the DNB Otorhinolaryngology degree from New Delhi, India.
Updated On:December 21, 2023
Read more.
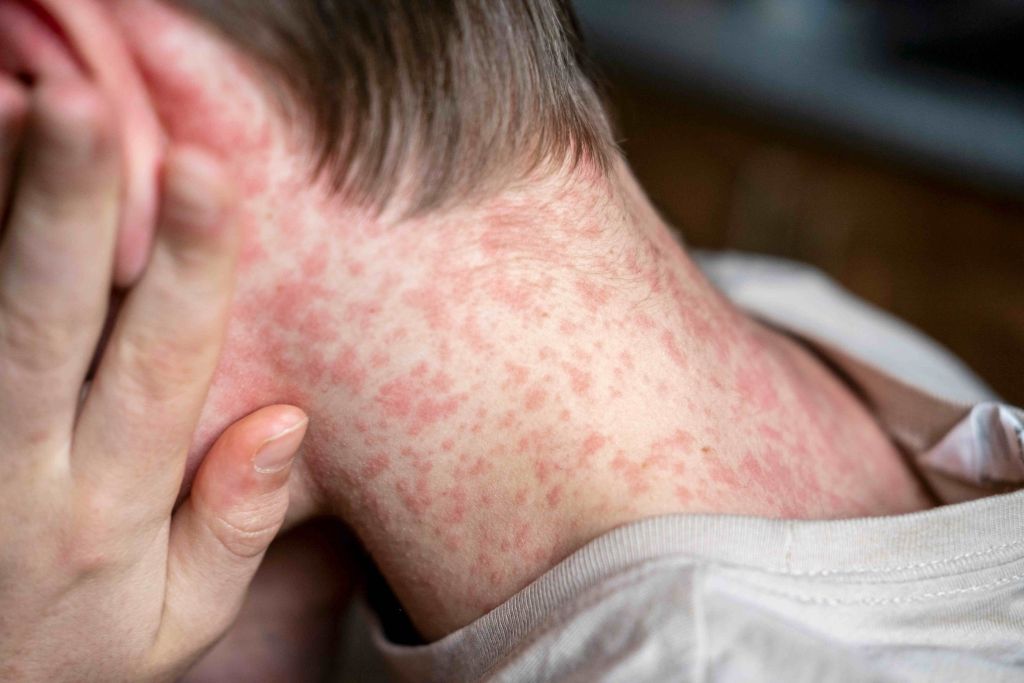
What is Tonsillitis?
The palatine tonsils are a pair of lymph nodes located at the back of the throat. One on the left, one on the right. Together, they play an essential role in protecting the body against respiratory & gastrointestinal infections & are part of the body’s immune system. Tonsillitis is a condition characterised by infection or inflammation of the tonsils. It is most common in childhood, but tonsillitis can occur at any age. Tonsillitis symptoms include sore throat, swollen tonsils, & a fever. Tonsillitis is a contagious condition, caused by common viruses & bacteria, such as Streptococcal bacteria, which causes ‘strep throat’. Left untreated, bacterial tonsillitis caused by strep throat can lead to some severe complications. Acute viral tonsillitis averagely goes away on its own after 4 to 10 days. Tonsillitis lasting longer than ten days, or recurring multiple times a year, is known as chronic or recurrent tonsillitis. Chronic tonsillitis can also cause tonsil stones, where materials like dead cells, saliva, & food build-up in tonsil crevices & harden into small stones.
Causes of Tonsillitis
Usually, tonsillitis is the result of a virus. But bacteria can also cause tonsillitis - group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS) - which also causes strep throat. Fungi or parasites cause some rare cases of tonsillitis. Tonsillitis spreads via air droplets from an infected person’s breath, coughs & sneezes. It spreads by breathing in infected air droplets, by getting them on the skin or on anything that comes into contact with the mouth, nose, or eyes. Symptoms usually appear a few days after exposure. Someone with tonsillitis caused by strep bacteria is contagious early on &, without treatment, can remain so for up to a fortnight. But treatment with antibiotics shortens the contagious period. Those infected are no longer contagious around 24 to 48 hours after taking antibiotics.
When to See your Doctor for Tonsiliitis
While tonsillitis is a common condition, if symptoms persist, visit your Medcare hospital or clinic where tests can be quickly & easily performed to ascertain whether the cause is viral or bacterial. Depending on the cause, a course of treatment will be recommended. In many cases, rest & self-care will resolve your tonsillitis. But in some cases, antibiotics or even removal of the tonsils is recommended. Your Medcare experts will be able to recommend the appropriate treatment plan.
Tonsillitis Signs & Symptoms
A sore throat is often the main symptom of tonsillitis. If symptoms feel like a cold, such as a runny or blocked nose, sneezing & coughing, a virus is most likely the cause. A sore throat, plus sudden, severe fever & swollen lymph nodes, without cold symptoms, is more likely to be a bacterial infection, which means you should see a doctor, & probably require a strep test & a course of antibiotics.
Common Signs & Symptoms of Tonsillitis include:
- Red, swollen tonsils with pus
- Raw, bleeding patches on the tonsils
- Difficulty swallowing
- Fever
- Bad breath
- Nasal congestion & runny nose
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Headache
- Abdominal pain
Bacterial infections will show symptoms, including a sore throat, with at least two of the following:
- A fever of 38.3°C (101°F) or higher
- White or yellow coating on the tonsils
- Swollen, tender tonsils
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- A rash
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Severe difficulty swallowing
- Pain on only one side of the throat
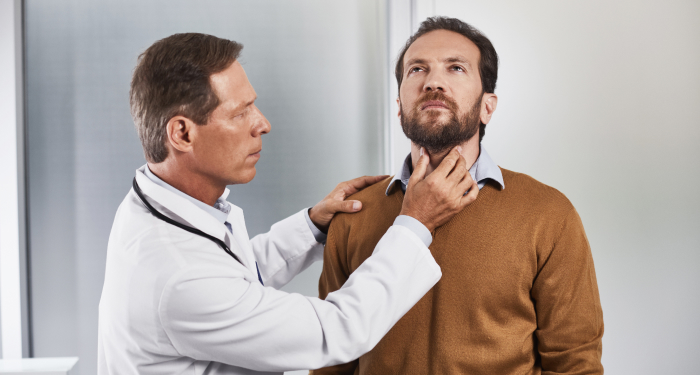
Diagnosis of Tonsiliitis
A doctor will examine the throat to see if the tonsils are red & swollen, with spots or sores. These are signs &U symptoms of tonsillitis. A rapid strep test may be conducted, & a throat culture taken, if streptococcus bacterial infection is suspected. Expect some questions regarding recent health & longer-term history of past throat infections. If tonsillitis occurs frequently, choice of treatment may include removal of the tonsils. There may also be a test for mononucleosis. Mononucleosis, or glandular fever, is a common illness caused by a virus, spread by saliva. Often seen in teens & young adults, it causes a bad sore throat, swollen neck glands, & a fever.
Tonsiliitis Treatment
Viral, acute tonsillitis caused by a virus will usually go away on its own within ten days. Throat pain can be alleviated by drinking plenty of fluids such as warm teas over-the-counter pain medicine, & other home treatments, as listed below. If your tonsillitis is bacterial, antibiotic treatment may be recommended. Medcare, & many other medical professionals, only suggest surgery to remove tonsils (tonsillectomy) when serious tonsil problems are apparent. These include recurrent infection (chronic tonsillitis) or long-lasting infections that do not heal & hinder everyday activities.
Tonsillectomy
Surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is a fairly common procedure, particularly for children, but isn’t performed as often as it used to be. Tonsillectomy might be considered when serious complications, recurrent infections, or chronic infections that do not respond to treatment & interfere with normal daily activities are present. For some children, tonsillectomy can greatly improve quality of life. Children most likely to benefit from tonsillectomy are those who have:
- Seven or more episodes of tonsillitis in a year.
- Five or more episodes a year for the past two years.
- Three or more episodes a year for the past three years.
Tonsillectomy is more likely when some of these episodes result in missing school, trouble sleeping, or suffering from other issues, such as:
- Tonsillitis lasting longer than three months, despite medication
- Obstructed air passages
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty talking because of nasal obstruction
- Tonsils that bleed heavily
Home Remedies for Tonsillitis
Home treatments such as drinking warm tea & taking over-the-counter pain medicine may help relieve discomfort. Home treatment can ease sore throats, & symptoms such as a runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing, & coughing.
Home Remedies for Tonsillitis Include:
- Regular gargling with warm salt water (in children aged eight or older)
- Drinking warm liquids (whichever feels better)
- Eating flavored ice pops, such as popsicles
- Getting plenty of rest
- Using a vaporizer or humidifier in the bedroom
- Using throat lozenges
- Using throat sprays & gargles
Foods to Eat when You have Tonsillitis
Most tonsillitis sufferers naturally tend to favour soft, liquid & cold foods. These include:
- Soup
- Pasta
- Scrambled or boiled eggs
- Mashed potato or other root vegetables
- Porridge
- Soft boiled vegetables & stewed fruits
- Ice cream
- Frozen yogurt
- Smoothies
Mint chewing gum can have a soothing effect on a sore throat. Harder foods – which may cause irritation or scratch an already sensitive throat, are best avoided, such as:
- Chips/crisps
- Acidic fruit juices & soda
- Alcohol & coffee
- Crusty bread
- Crackers
- Dry cereal
- Toast
- Raw carrots & apples
- Spicy or especially rich foods
Risk Factors for Tonsillitis
Unfortunately, most children have a susceptibility to contracting tonsillitis. Instilling good hygiene practices in children from an early age helps avoid the condition, but the main risk factors include:
- Age: Tonsillitis mostly affects children, between ages 5 & 15.
- Frequent exposure to germs: School-age children are in unfortunately close contact with other children & are frequently exposed to the viruses &/ or bacteria that can cause tonsillitis.
- Close contact with an infected person
- Touching an object or surface that has recently been touched or used by an infected person
- Nasal obstruction: Which causes you to breathe through the mouth
Tonsillitis Complications
Tonsillitis caused by strep bacteria that is untreated or not treated with antibiotics may result in complications, such as:
Peritonsillar Abscess
Peritonsillar abscesses, pockets of infection outside the tonsils, are a potentially serious complication of tonsillitis. These abscesses form when a bacterial infection spreads from infected tonsils to the surrounding area. Symptoms include:
- A severe sore throat that feels worse on one side
- Mouth & throat swelling
- Difficulty speaking
- Trouble swallowing
- Breathing issues
- Difficulty opening the mouth
- Swollen lymph gl&s
- Fever & chills
- Earache or neck pain on the same side as the sore throat
Without urgent treatment, a peritonsillar abscess can lead to sepsis & severe breathing difficulties, which can both be life-threatening. Other more serious complications, such as rheumatic fever, are rare. Recurrent & ongoing (chronic) tonsillitis may obstruct the upper airway & cause problems, such as:
- Snoring
- Nasal congestion
- Mouth breathing
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Heart & lung problems
Tonsillitis Prevention
A wide variety of viruses & bacteria cause tonsillitis, so follow basic health & hygiene precautions to help prevent contracting & spreading tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis prevention steps are especially helpful for children:
- Avoid close contact with other sick children, or those displaying symptoms.
- Practice proper hand-washing, & good bathroom habits with the children.
- Tell your child not to share toothbrushes or eating utensils with other children.
- Regularly clean & disinfect surfaces & toys.
- Teach children to cover their mouths when coughing or sneezing, ideally using a tissue, so germs don’t get on their hands.
- Disposable wipes & h& sanitizer are a must to help stop the spread of germs.
- Clean public items & surfaces: Spray sanitizer or use a disinfecting wipe on objects & places that you & your child may touch - such as shopping carts & public bathrooms.
Meet our doctors from the Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) department
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
Similar Posts
teleMEDCARE App
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Chronic Care
Know more about our Chronic Care Management Programme in partnership with Damana Saicohealth.

teleMEDCARE App mobile
Download teleMEDCARE app from Google Play or App Store to connect immediately to Medcare doctors at a click of a button and without an appointment.

Home Services
We offer our patients a broad range of home health care services in the comfort of their own homes. Book an appointment for lab tests, vaccinations, nurses and physiotherapists.

Spotii
We have partnered with Spotii to offer a more flexible way to pay - Pay over time for your purchase. No interest, no cost & no catch.